GitLab Getting Started
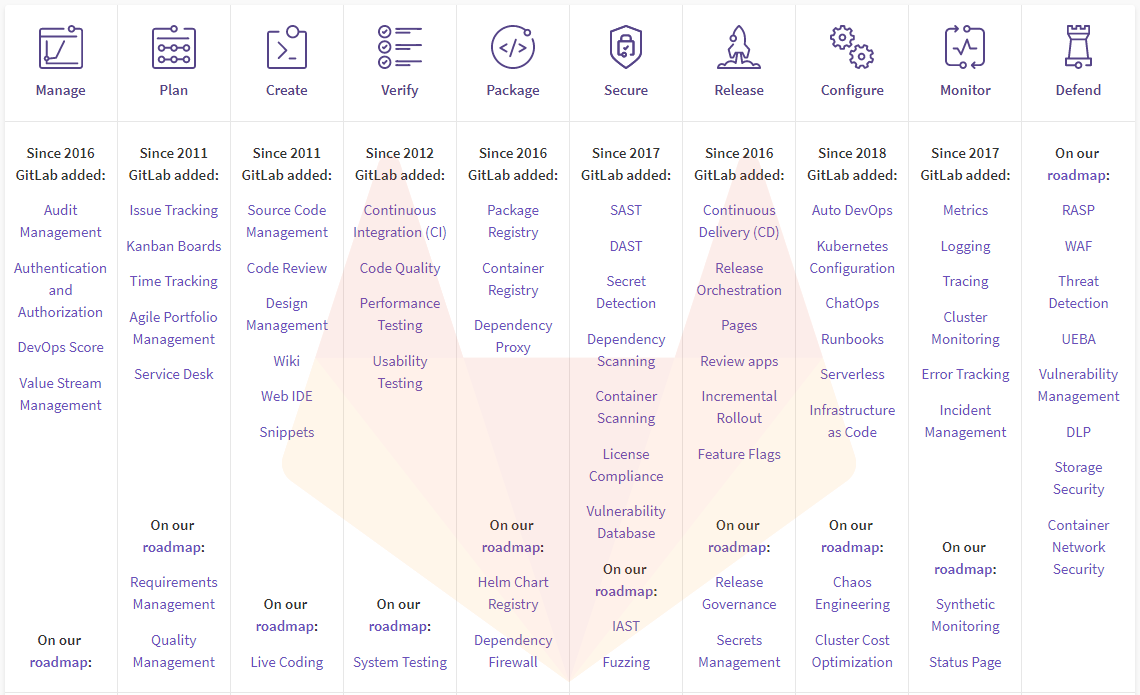
GitLab is a complete DevOps platform. With GitLab, you get a complete CI/CD toolchain out-of-the-box. One interface. One conversation. One permission model. Thousands of features. You'll be amazed at everything GitLab can do today.
If you have installed Websoft9 GitLab, the following steps is for your quick start
Preparation
- Get the Internet IP of your Server on Cloud
- Check your Inbound of Security Group Rule of Cloud Console to ensure the TCP:80 is allowed
- Connect your Server and get default username and password of GitLab
- Complete Five steps for Domain if you want to use Domain for GitLab
GitLab Getting Started
Steps for you
-
Using local browser to visit the URL http://DNS or http://Server's Internet IP, access login page
-
Input user and password(Don't have password?),go to GitLab dashboard to start use it
-
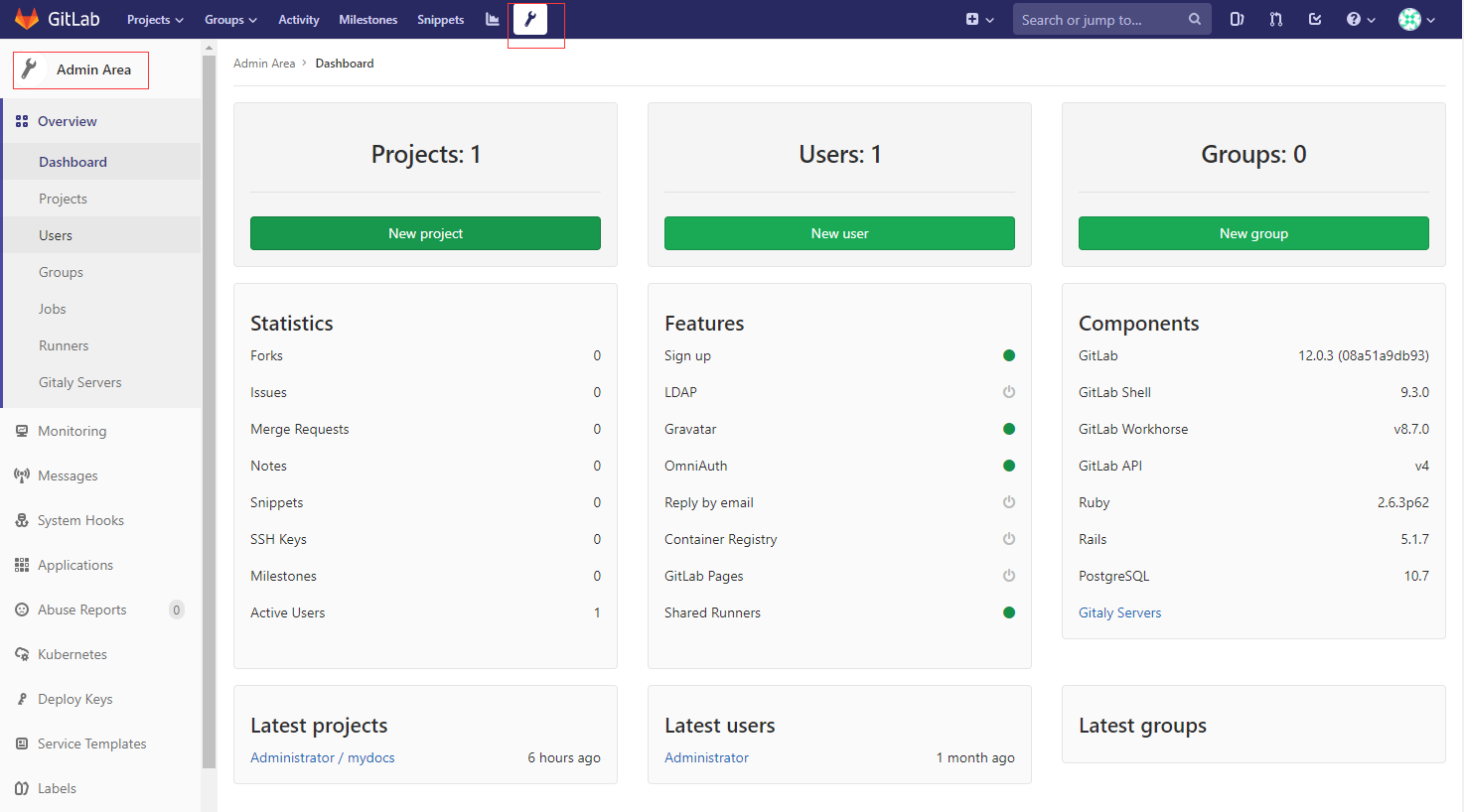
Go to GitLab Admin Area to configure it
-
Open: User Settings > Preferences to set your language
-
Open: User Settings > SSH key to set your keys
-
If you have installed GitLab-EE, go to 【Admin Area】>【License】, import your license or try it
More useful GitLab guide, please refer to GitLab Documentation
Having trouble?
Below is for you to solve problem, and you can contact Websoft9 Support or refer to Troubleshoot + FAQ to get more.
GitLab interface 502 error?
Refer to:here
GitLab need long time to start?
Refer to:here
GitLab QuickStart
This task【Manage team, member and code in GitLab】 is for your GitLab QuickStart
-
Domain binding, the complete real path needs to be used in the subsequent project management. After Gitlab is installed, the default domain name is http://gitlab.example.com, you need to modify it to your existing domain name in the configuration file, or modify it to IP to access http://IP. ReferenceDomain binding。
-
Project management: The administrator creates a new project, initializes the project, adds a development branch "dev", and does not open the master branch master to developers
Create project: Websoft9-Site1
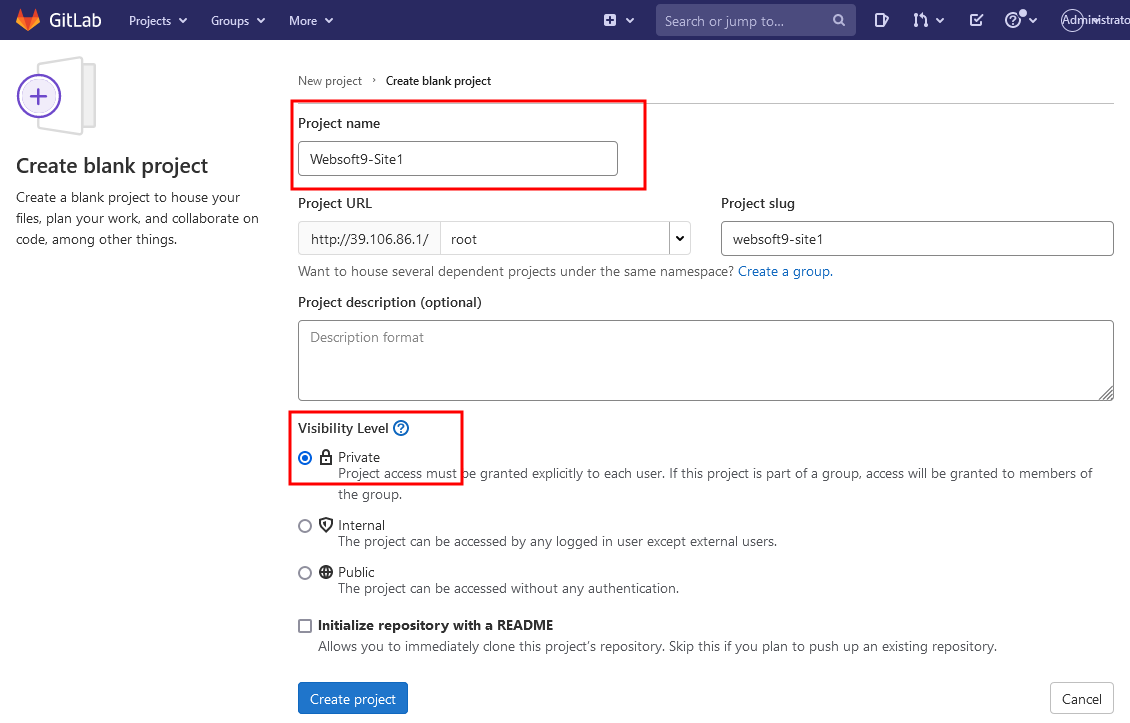
Initialize the project, add README.md and index.html pages, and submit
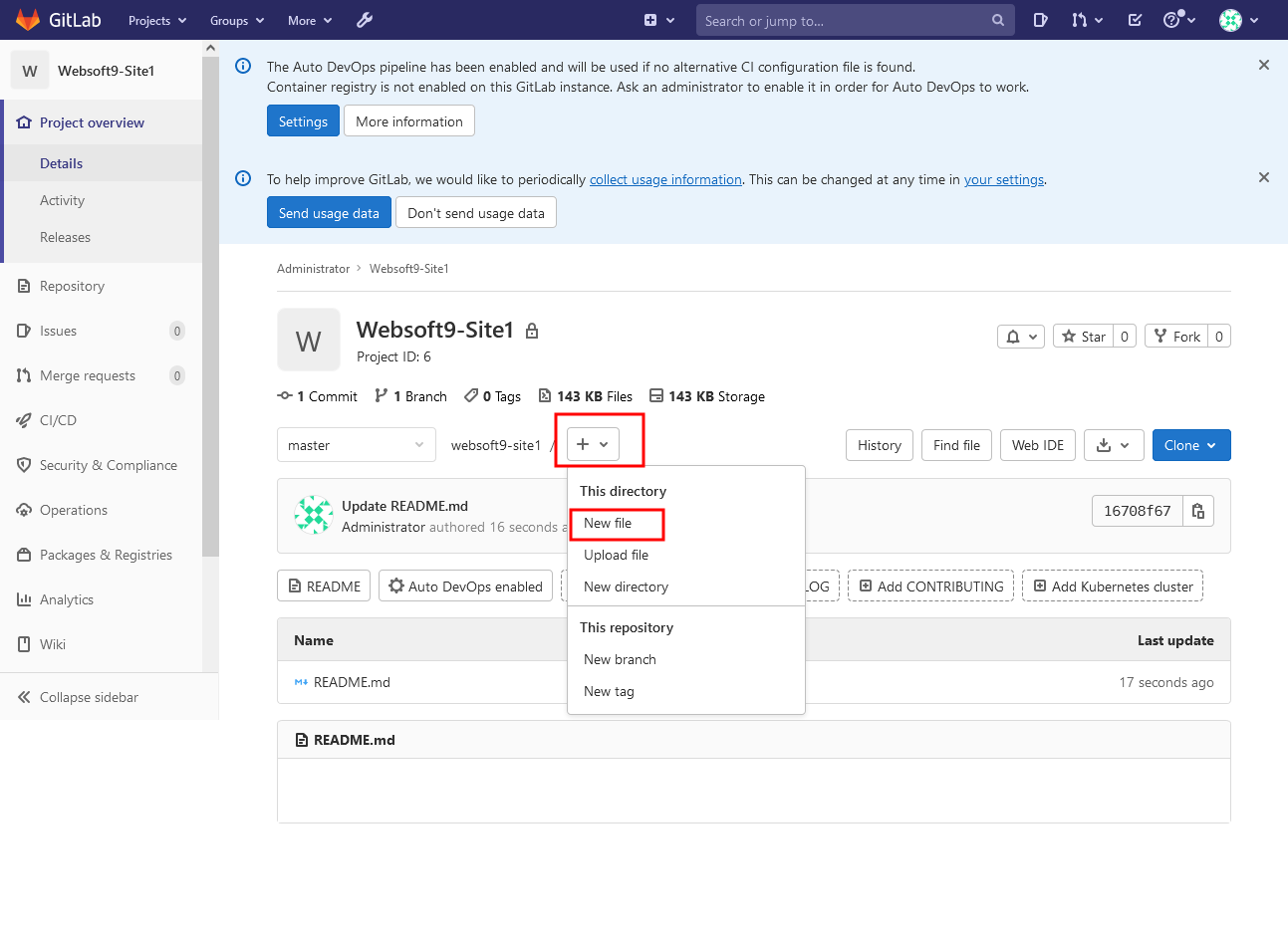
New development branch dev
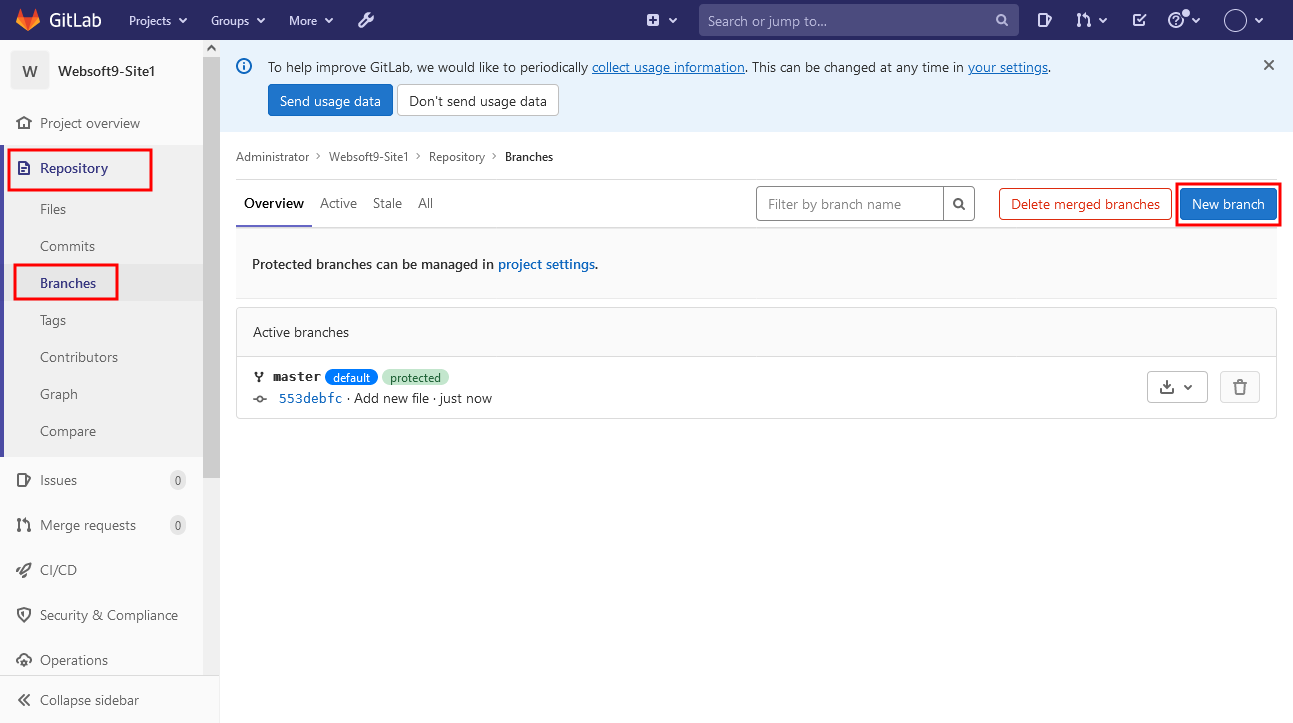

-
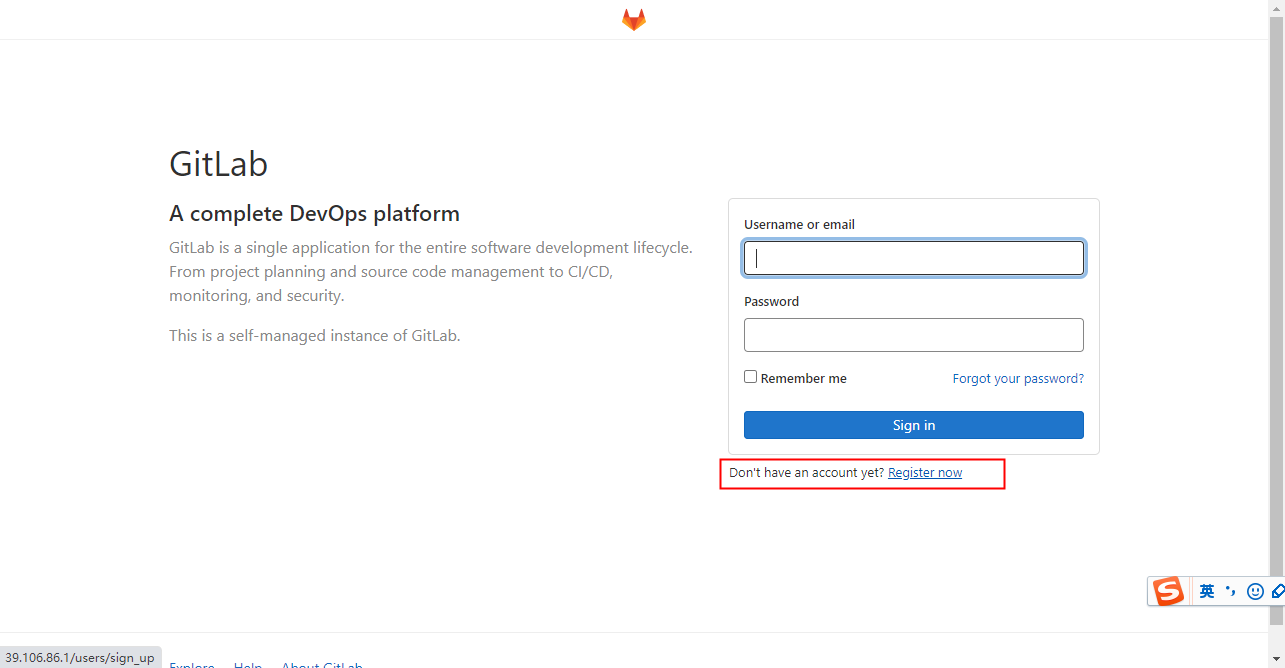
Member management: team members register an account on the login page. The administrator activates users in the system, and then invites users among project members and configures permissions. The user must be activated to log in to the system.
User registration
Administrator activates registered users
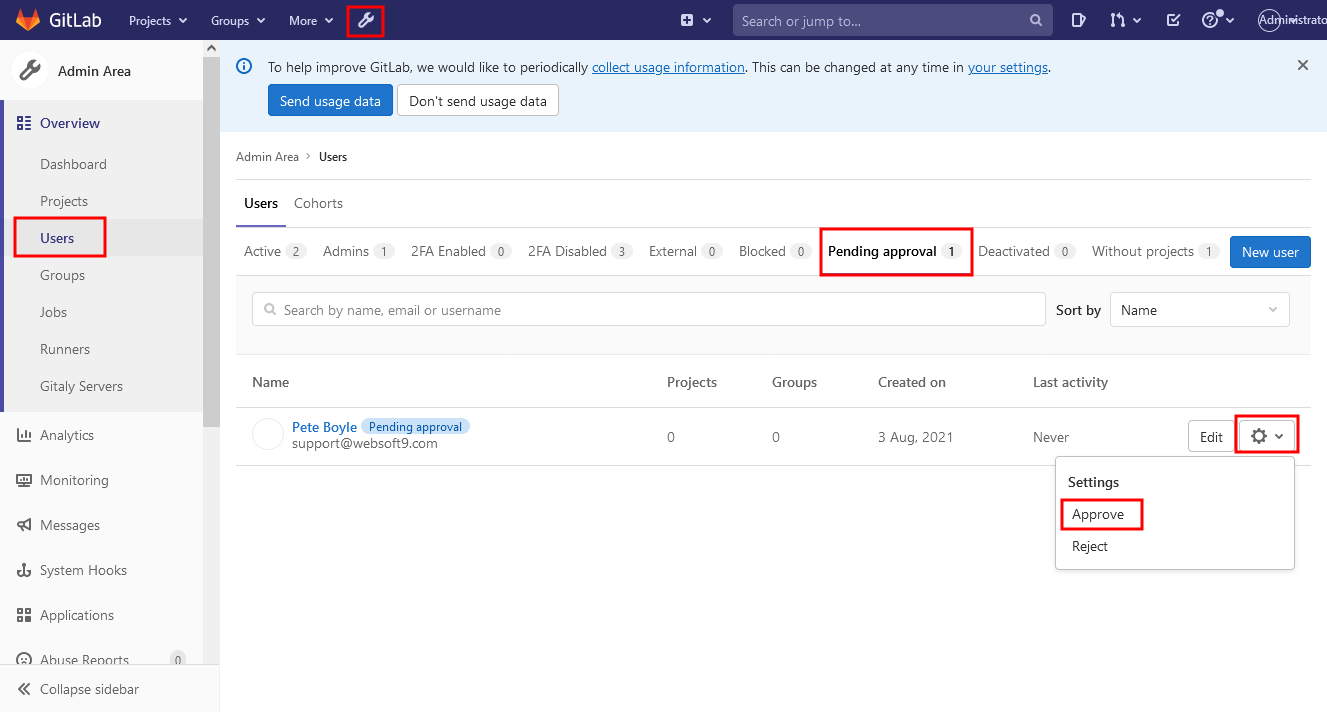
The administrator invites users to join the project group and assigns rights
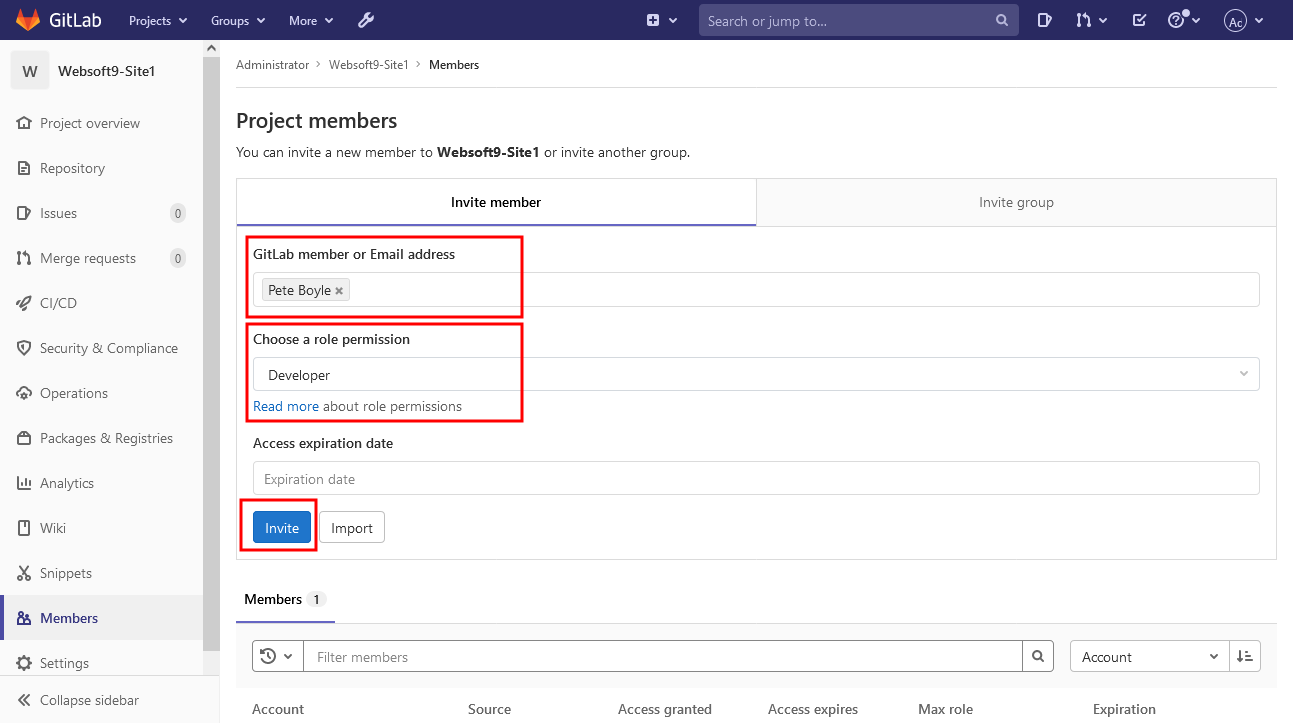
-
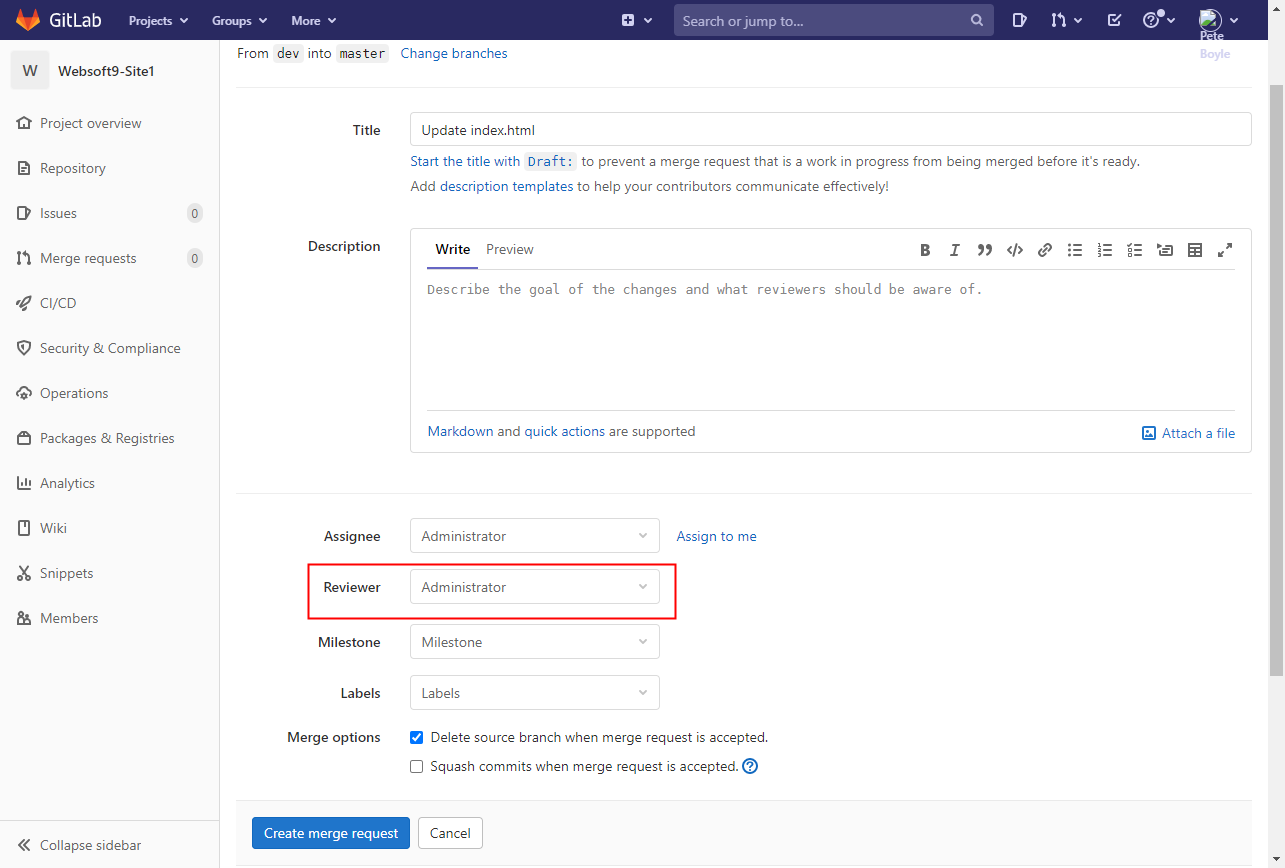
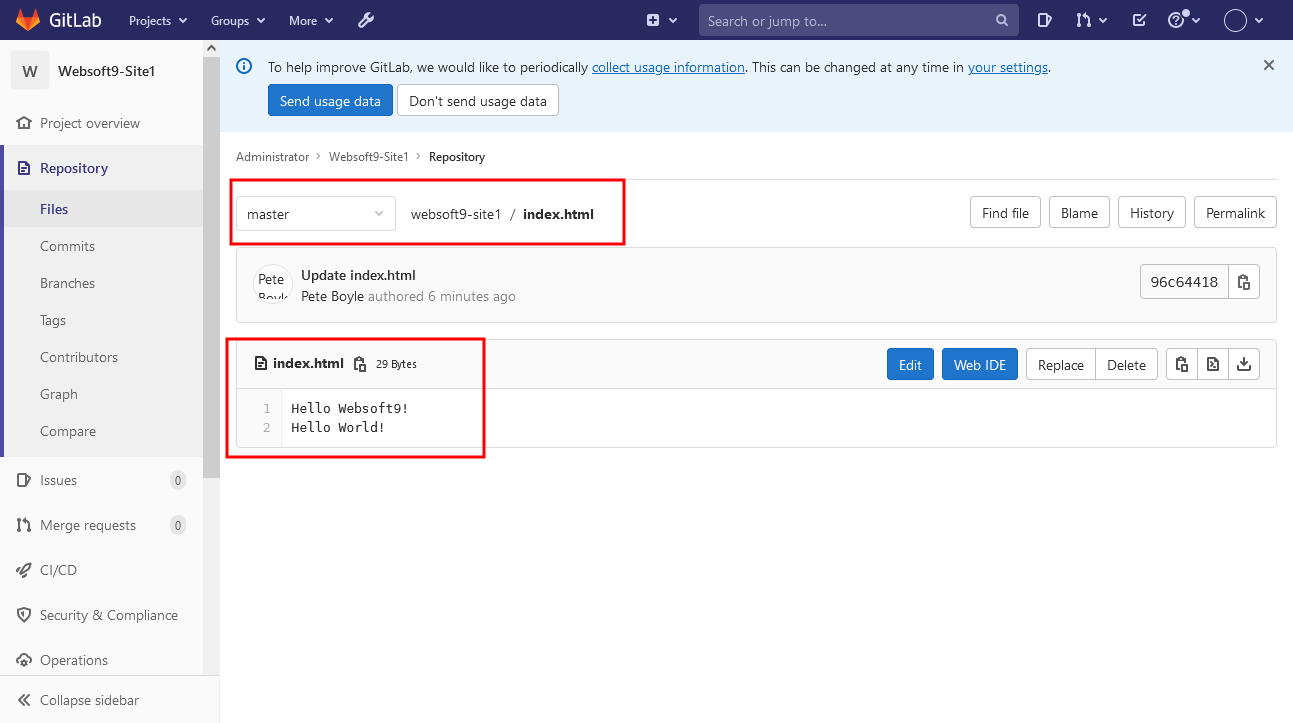
Code management: Project members are responsible for the development of the "index.html" page, through git clone the project to the local, development in vs code. Use the "Git Base" and clone the project locally via "git clone"

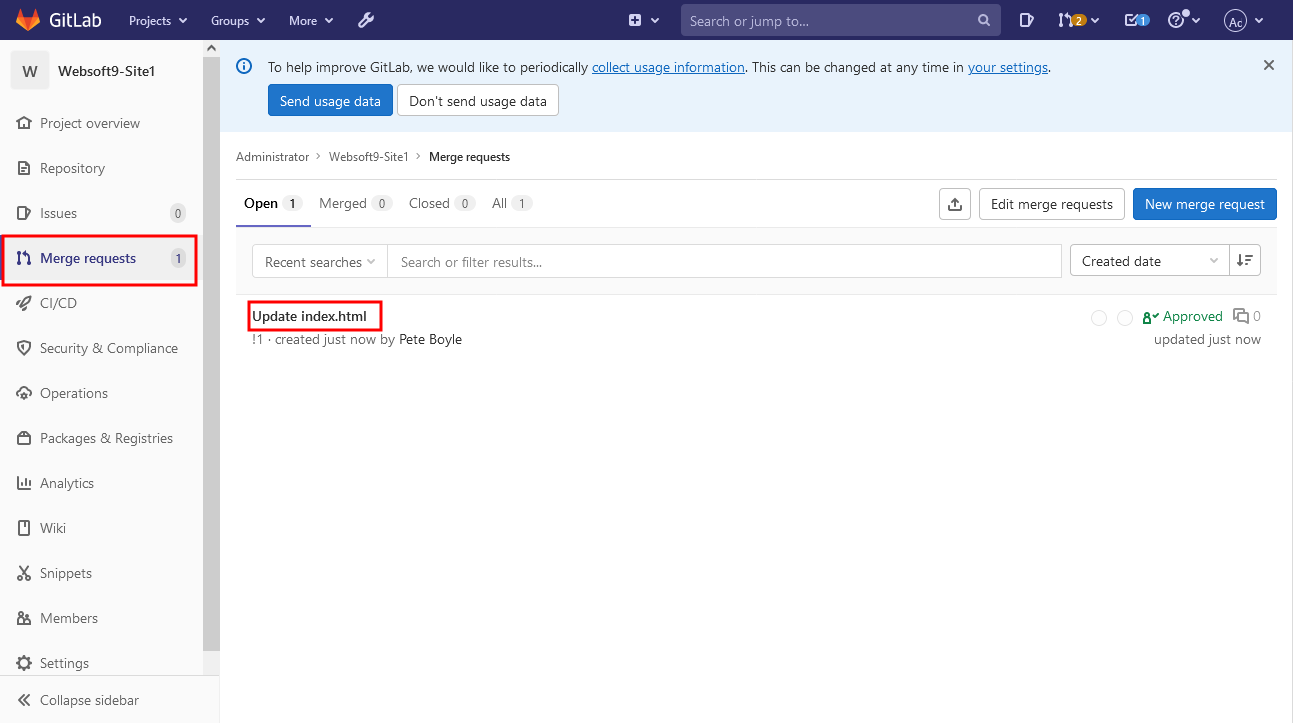
Use vs code to edit index.html locally, and then submit the local code to the server. Log in to gitlab with your development account, view updates and create a merge request

Administrator login Gitlab merge request

Gitlab Setup
Set GitLab repository address
In the prepare link before initialization, if you have completed the domain five-step setup, GitLab can access the domain name, but the URL of the GitLab repository is still Not the user's own domain name.
Therefore, you also need to refer to the following steps setting the GitLab repository address:
- Log in to the cloud server via SSH or SFTP
- Modify the GitLab configuration file, and change the value of the external_url item http://gitlab.example.com to your domain name
external_url "http://gitlab.example.com" # Change to custom domain name
... - Save the configuration file and restart the following services
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
Set HTTPS for GitLab repository
The HTTPS of the GitLab repository is not equivalent to the HTTPS of GitLab itself, and additional settings are required beforehand: Enabling HTTPS
Configure SMTP
Sending mail is a common feature for GitLab. After a large number of user practice feedback, only one way is recommended, that is, using the third-party STMP service to send the email.
Do not try to install Sendmail or other Mail server software on your Cloud Server for sending mail, because it is very difficulty in maintenance.
Follow is the sample using SendGrid's SMTP Service to configure sending mail for GitLab:
- Log in SendGrid console, prepare your SMTP settings like the follow sample
SMTP host: smtp.sendgrid.net
SMTP port: 25 or 587 for unencrypted/TLS email, 465 for SSL-encrypted email
SMTP Authentication: must be checked
SMTP Encryption: must SSL
SMTP username: websoft9smpt
SMTP password: #fdfwwBJ8f - Use SSH or SFTP to connect Server, modify the GitLab configuration file: /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
gitlab_rails['smtp_enable'] = true
gitlab_rails['smtp_address'] = "smtp.sendgrid.net"
gitlab_rails['smtp_port'] = 587
gitlab_rails['smtp_user_name'] = "a_sendgrid_crendential"
gitlab_rails['smtp_password'] = "a_sendgrid_password"
gitlab_rails['smtp_domain'] = "smtp.sendgrid.net"
gitlab_rails['smtp_authentication'] = "login"
gitlab_rails['smtp_enable_starttls_auto'] = true
gitlab_rails['smtp_tls'] = false - Restart Service
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
GitLab provides configuration methods for dozens of different SMTP service providers, please refer to the official documentation:SMTP settings
Reset admin password
When you forget the administrator password, please refer to the following scheme to reset the password (source of the scheme):
- Log in to the GitLab server using SSH
- Enter the
gitlab-rails consolecommand and follow the prompts to complete the next steps
$ gitlab-rails console
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ruby: ruby 2.7.2p137 (2020-10-01 revision 5445e04352) [x86_64-linux]
GitLab: 13.8.4 (9fb9cbf50c3) FOSS
GitLab Shell: 13.15.1
PostgreSQL: 12.5
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Loading production environment (Rails 6.0.3.4)
irb(main):001:0>
irb(main):002:0> user = User.find_by_username 'root'
=> #<User id:1 @root>
irb(main):003:0> user.password='Websoft9' //修改密码
=> "Websoft9"
irb(main):004:0> user.password_confirmation='Websoft9'
=> "Websoft9"
irb(main):006:0> user.save!
Enqueued ActionMailer::MailDeliveryJob (Job ID: 3f4ac447-9869-412a-9b5a-988c06cf eaa2) to Sidekiq(mailers) with arguments: "DeviseMailer", "password_change_by_ad min", "deliver_now", {:args=>[#<GlobalID:0x00007fb7e5337990 @uri=#<URI::GID gid: //gitlab/User/1>>]}
=> true
irb(main):007:0>
Reference sheet
The below items and General parameter sheet is maybe useful for you manage GitLab
Below is a simplified architecture diagram that can be used to understand GitLab's component architecture.
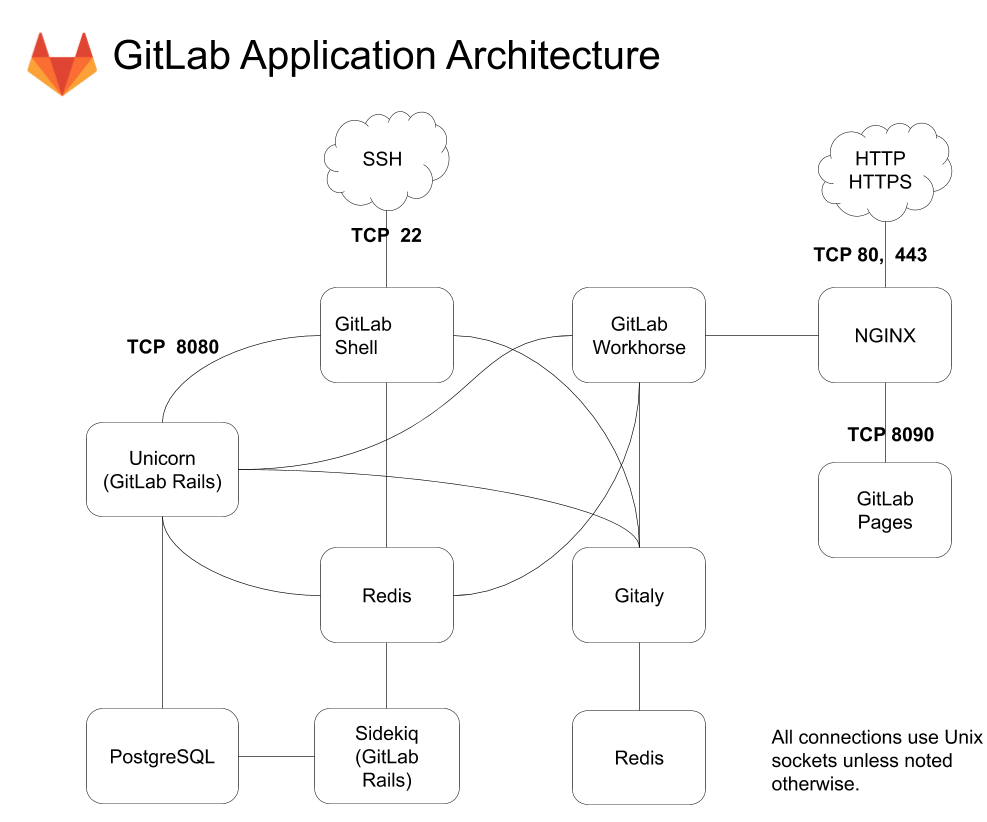
-nginx: static web server. -gitlab-shell: Used to process Git commands and modify the list of authorized keys. -gitlab-workhorse: Lightweight reverse proxy server. -logrotate: logs file management tool. -postgresql: database. -redis: cache database. -sidekiq: Used to execute queued tasks in the background (asynchronous execution). -unicorn: An HTTP server for Rack applications on which GitLab Rails applications are hosted.
GitLab includes dozens of components (view), view the server via /opt/gitlab/version-manifest.txt All component names and versions above
Run docker ps, view all containers when GitLab is running:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
c5b22639c668 gitlab/gitlab-ce:latest "/assets/wrapper" 2 hours ago Up 2 hours (healthy) 443/tcp, 0.0.0.0:23->22/tcp, :::23->22/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9001->80/tcp, :::9001->80/tcp gitlab
49995b282a20 gitlab/gitlab-runner:latest "/usr/bin/dumb-init …" 2 hours ago Up 2 hours gitlab-runner
Path
GitLab
GitLab installation directory: /data/apps/gitlab
GitLab data directory: /data/apps/gitlab/data/gitlab_data
GitLab log directory: /data/apps/gitlab/data/gitlab_logs
GitLab configuration file: /data/apps/gitlab/data/gitlab_config/gitlab.rb
Port
In addition to common ports such as 80, 443, etc., the following ports may be used:
No special port
Version
docker exec -i gitlab head -n+1 /opt/gitlab/version-manifest.txt
Service
sudo docker start | stop | restart | stats gitlab
sudo docker start | stop | restart | stats gitlab-runner
CLI
GitLab provides the command line tool gitlab-ctl for comprehensive management and configuration of GitLab
$ docker exec -it gitlab gitlab-ctl -h
I don't know that command.
omnibus-ctl: command (subcommand)
check-config
Check if there are any configuration in gitlab.rb that is removed in specified version
deploy-page
Put up the deploy page
diff-config
Compare the user configuration with package available configuration
get-redis-master
Get connection details to Redis master
prometheus-upgrade
Upgrade the Prometheus data to the latest supported version
remove-accounts
Delete *all* users and groups used by this package
reset-grafana
Reset Grafana instance to its initial state by removing the data directory
set-grafana-password
Reset admin password for Grafana
upgrade
Run migrations after a package upgrade
upgrade-check
Check if the upgrade is acceptable
General Commands:
cleanse
Delete *all* gitlab data, and start from scratch.
help
Print this help message.
reconfigure
Reconfigure the application.
show-config
Show the configuration that would be generated by reconfigure.
uninstall
Kill all processes and uninstall the process supervisor (data will be preserved).
Service Management Commands:
graceful-kill
Attempt a graceful stop, then SIGKILL the entire process group.
hup
Send the services a HUP.
int
Send the services an INT.
kill
Send the services a KILL.
once
Start the services if they are down. Do not restart them if they stop.
restart
Stop the services if they are running, then start them again.
service-list
List all the services (enabled services appear with a *.)
start
Start services if they are down, and restart them if they stop.
status
Show the status of all the services.
stop
Stop the services, and do not restart them.
tail
Watch the service logs of all enabled services.
term
Send the services a TERM.
usr1
Send the services a USR1.
usr2
Send the services a USR2.
Gitlab Geo Commands:
geo
Interact with Geo
geo-replication-pause
Replication Process
geo-replication-resume
Replication Process
promote-db
Promote secondary PostgreSQL database
promote-to-primary-node
Promote to primary node
promotion-preflight-checks
Run preflight checks for promotion to primary node
replicate-geo-database
Replicate Geo database
set-geo-primary-node
Make this node the Geo primary
Pgbouncer Commands:
pgb-console
Connect to the pgbouncer console
pgb-kill
Send the "resume" command to pgbouncer
pgb-notify
Notify pgbouncer of an update to its database
pgb-resume
Send the "resume" command to pgbouncer
pgb-suspend
Send the "suspend" command to pgbouncer
Database Commands:
get-postgresql-primary
Get connection details to the PostgreSQL primary
patroni
Interact with Patroni
pg-password-md5
Generate MD5 Hash of user password in PostgreSQL format
pg-upgrade
Upgrade the PostgreSQL DB to the latest supported version
revert-pg-upgrade
Run this to revert to the previous version of the database
set-replication-password
Set database replication password
write-pgpass
Write a pgpass file for the specified user
Consul Commands:
consul
Interact with the gitlab-consul cluster
Container Registry Commands:
registry-garbage-collect
Run Container Registry garbage collection.
Let's Encrypt Commands:
renew-le-certs
Renew the existing Let's Encrypt certificates
Gitaly Commands:
praefect
Interact with Gitaly cluster
Backup Commands:
backup-etc
Backup GitLab configuration [options]
API
GitLab 提供多种 API 方式,包括:REST API, SCIM API, GraphQL API
curl "https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects"